Aleph Zero Bridges: Introducing MOST
Jan 11, 2024

Learn about Aleph Zero’s bridge to Ethereum (ETH) and how it fits within the broader scope of the network’s interoperability.
We’re happy to officially announce the advanced status of works carried out on MOST, the bridge between Aleph Zero and Ethereum. MOST will be the main gateway to Ethereum, enabling external liquidity and stablecoins to be moved to Aleph Zero while letting DeFi flourish on-chain.
MOST: the gateway to Ethereum and Aleph Zero
Drawing inspiration from the most simple and secure designs in the space, MOST is poised to help make Aleph Zero’s strategy robust and more independent while addressing the immediate concerns of interoperability.
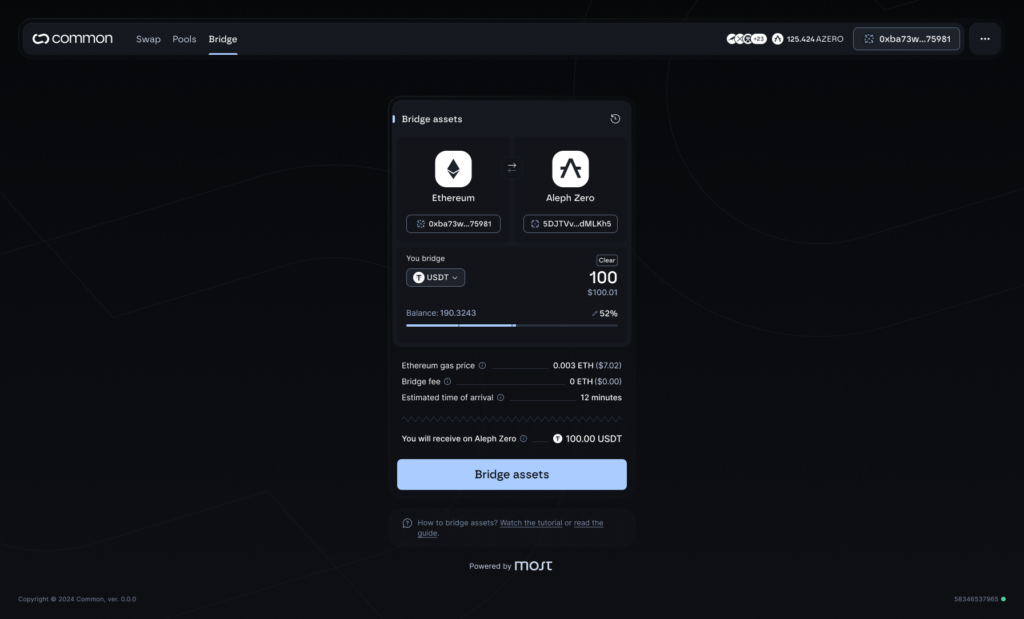
MOST’s intuitive design and accessibility will help users seeking a straightforward way to move assets between Ethereum and Aleph Zero. It’s a guardian-based bridge, with each guardian maintaining two instances of the setup — one for the Testnet, and one for the Mainnet. Eight guardians will be onboarded in total, enabling sufficient decentralization of this product.
Guardians will have control over two governance keys (one for Aleph Zero, and one for Ethereum) as a part of a multisig wallet that can be used to change the composition of the guardian committee, perform contract upgrades, and more.
Among the features of this design are reduced fees for bridging native ETH, stablecoins, and tokens from Ethereum to Aleph Zero to incentivize attracting liquidity to be used within the Aleph Zero ecosystem.
MOST has been under development since September, 2023, with a primary focus on the design security, simplicity, and ease of use. Work on the bridge is currently at an advanced stage, with the source code to be made public in the coming weeks to cater to the ethos of building in public. Once the development is concluded, the code will be externally audited in a way that ensures highest security standards.
And where does the name come from? “Most” is the word for “bridge” in many Slavic countries, namely in Polish, Czech, Slovak, Slovenian, Croatian, Serbian, and Bulgarian. Interestingly enough, in German, for instance, it translates to juice, in Hungarian to now, and in Austria, that is… a young wine.
MOST as one of three components
Aleph Zero’s bridging strategy encompasses three key components: the introduction of Most as a convenient and cheap Ethereum bridge, the integration with the innovative, Coinbase-backed Router Protocol, as well as the previously announced zParachain bridge to the Polkadot ecosystem.
Router Protocol: bridging with intent
In parallel, our collaboration with the Router Protocol introduces a versatile bridging option to a variety of ecosystems such as Ethereum, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche, Fantom, Aurora, Kava, Base, Arbitrum, Rootstock, Near, Moonbeam, and Moonriver, with more blockchains to come in the near future.
Moreover, Router Protocol is working on a Cross-chain Intent Framework (CCIP), a novel paradigm designed to abstract the processes involved in executing complex workflows, such as cross-chain staking. As we can read in the CCIP whitepaper,
“By deriving explicit, programmable intents from ambiguous user intents, disintegrating convoluted interactions into manageable sub-interactions, and instituting a standard interface for dApps through intent adapters, this framework endeavors to streamline user-dApp interactions significantly. The proposed framework will enhance user experience, expedite the adoption of Web 3.0 applications, and facilitate application development without necessitating a deep understanding of the underlying dApp complexities.”
CCIP Whitepaper, Router Protocol
In January, 2024, Router’s team successfully deployed a Gateway Contract on the Alpha network, marking a significant step forward in the integration of Aleph Zero and Router Protocol.
Router Protocol design, as reported by the team, aims to encompass enhanced security features, fast transaction speeds, and the ability to handle seamless cross-chain swaps.
Router Protocol is backed by Coinbase Ventures, QCP Capital, Defi Capital, Mapleblock, Wintermute, Polygon, Shima Capital, and others.
zParachain bridge
First, a quick reminder. Aleph Zero’s (AZERO) is not a parachain, nor will it become one. The parachain slot obtained by the team will be used only for bridging purposes between Polkadot and Aleph Zero ecosystems, creating an intermediary parachain between these two networks.
The Aleph Zero “zParachain” will operate with GRANDPA consensus and connect Aleph Zero Mainnet to the Polkadot ecosystem, with XCM messaging to be used across the Polkadot and its parachains. This bridge will be based on light-client, meaning the finality of transactions from the source chain can be verified on the target chain instead of requiring a third-party component.
Why this matters
The bridging strategy aims to offer versatility, stability, and several options to choose from, depending on who the end user is. No blockchain is an isolated island, and Aleph Zero is no different — but user security and experience need to be prioritized above all.
Stay tuned for the upcoming updates about Aleph Zero bridges!

